How Classes work in JavaScript

Classes are the syntactic sugar in the javascript unlike the other programming languages javascript doesn’t contain proper classes.
Classes use the prototype-based inheritance by using constructors.
What is a constructor?
A constructor is a function object which is used to create and initializes the objects.

Let’s discuss now by using examples.
function Student(){}const student = Student();
console.log(student) // undefined
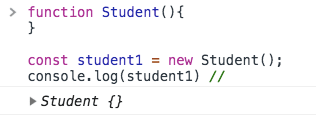
If we invoke a function with the new keyword it will return the empty object instead of undefined.
function Student(){
}const student1 = new Student();console.log(student1); // { }
How to add properties into that returned empty object?
function Student(name,age){ this.name = name
this.age = age
}const student1 = new Student('king',20)
// { name : 'king',age:20 }
The new object is created by the constructor and assigned to this keyword so that we can add the properties to the object by using this.propertyname.
At last, the constructor returns this object like the below image.

Classes
Classes are also a special type of functions using prototype-based inheritance. To declare the class we need to use the class keyword.
class Student{constructor(name,age){
this.name = name
this.age = age
}}const student1 = new Student('king',20)// { name : 'king',age:20 }
Methods in classes
class Student{ constructor(name,age){
this.name = name
this.age = age
} getAge(){
return this.age;
}}const student1 = new Student('king',20)
student1.getAge();
The methods we declare inside the Student class are added to its prototype and it assigns the methods to the this.__proto__ property. so that at the time of accessing the getAge method javascript engine first look on its object, if it fails to find then it will look up at the __proto__ property.
check out the below image you will get the clarity.

Extends in classes
Extends keyword helps us to access the properties and methods present in the other class or parent class.
super
If we extend the class from the parent class we need to invoke the parent class before using the child class there is a super method provided by the javascript, it does the invocation for us.
class Csestudent extends Student{ constructor(name,age,course){
super(name,age);
this.course = course
} getCourse(){
return this.course
}
}const student = new Csestudent('king',20,'JavaScript')
In the below image, I have shown how the javascript engine process the code.

Let me explain what happens when we invoke a Csestudent class javascript engine first adds the Csestudent to the call stack once it sees the super method it invokes the parent class which is a Student and it returns the object with two properties at final we are adding course property to that object.
The final student object might look like these.

But the methods we declared in the Student class are present in the this.__proto__.__proto__
References
Other tutorials
Originally Published at reactgo.com

